1.What is a transistor?
A junction transistor is simply a
sandwich of one type of semiconductor material between two layers of the other
type. A transistor is a three terminal current sensing device. It can be looked
upon as two pn junction placed back to back. The three terminals are named as
emitter base & collector.
2.What is BJT, explain
about its terminals, what are types, and which type is better, why?
Bipolar junction Transistor in this
corrent flows due to two polarities(electrons, holes), NPN or PNP type ,NPN is
best because mobility of electrons is more than mobility of holes so electron
current is more.
3.What are the different
configurations of transistor?
a) Common Emitter (CE) b) Common Base
(CB) c) Common collector (CC)
4.What is Common Base
configuration?
base is common between input and
output circuits. emitter-base terminal input signal is applied and in
collector-base terminal output is taken from it.
5.What are the
characteristics of CB?
since it has a low input resistance
and a high output resistance, current gain of less than 1. The input and output
signals in the common-base circuit are in phase
6.What is transistor and
why it is called like that?
Because it transfers the input signal
from low resistance to high resistance
7.Define α, β, γ, what is
the relation between them?
These are current gains in CB,CE,CC
configurations respectively,
;
αγ=
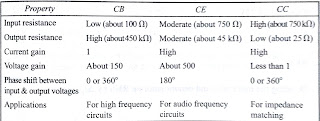
8.Compare CE,CC,CB
configurations?
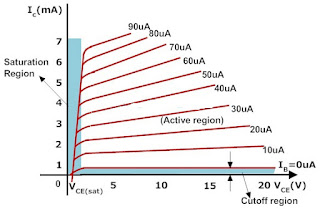
9.Define cut-off, active
and saturation regions?
Cut off- both emitter Je, collector
Jc junctions in Reverse bias
Active – Je forward, Jc Reverse bias
Saturation – Je,Jc in forward bias
10.What
do you understand by input and output characteristics?
characteristics gives the information about input resistance and output resistances.
11.Explain
the physical structure of a BJT?
One N type
material is sandwiched between two P type materials or One P type material is
sandwiched between two N type materials , widths (C>E>B), doping
concentration(E>C>B)
12.Explain
Early Effect?
The
variation in base width of BJT due to variation in the applied base- collector
voltage
13.Why
does the emitter current increase with increase in reverse bias at the
collector junction?
Due to
breakdown in collector junction
14.What
is meant by collector reverse saturation current?
Minority
carriers flow throw collector junction when it is connected in reverse bias
15.Write
the collector current expression for BJT in CB configuration?
Cutoff
region Ic=0
Active
regionIc= βIb
Saturation Ic<βIb
16.Give
the values of VCE Sat for the transistor BC107.
Vce
sat=0.2v
17.Explain
the performance of the transistor as
an electronic switch?
When
transistor is in cut off it works as off switch, when transistor is in
saturation it works as on switch
18.Is
the BJT Transistor a current controlled device or a voltage-controlled device?
Current
controlled current device
19.Draw
the symbolic representations of NPN and PNP transistors.
20.Sketch
the characteristics of a BJT in Common-Emitter Configuration.
21.Why
is it called Common-Emitter configuration?
Emitter
terminal is common to input and out put
22.What
is a “load-line”? What is its
significance? Differentiate between a.c.
load line and d.c. load line.
Load line specifies the operating
point, Dc load line is the line based on the relation between output voltage
and currents when input is zero, Ac load line is the line which pocess through
the Q point with slope of (-1/Rac, Rac= Rc//Rl)
23.What is meant by Q-
point?
It specifies the correct biasing at
which gives required amplification
24.What is Biasing and why
it is needed for transistor?
The process of giving proper supply
voltage and resistances for obtaining desired operating point
25.What are the methods of
transistor biasing, which type is best and why?
Fixed bias, Emitter feedback bias,
Collector to base bias, Collector- emitter feedback bias, self bias(voltage
divider bias), in these all self bias is best because it is more stable for a
greater range of input signal
26.What is thermal Runaway?
It is a situation where an increase
in temperature changes the conditions in a way that causes a further increase
in temperature.
27.Thermistor temperature
co efficient is?
It may be + or – based on the
material used.
28.Define two port
networks, types, which one is best for bjt and why?
Z, Y, h, g, ABCD parameters, best one
is hybrid parameters bczthethese gives all parameters about amplifier like
input, output impedance, voltage and current gains.
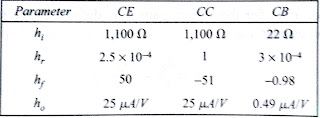
29.What are the typical
h-parameter values for a transistor?
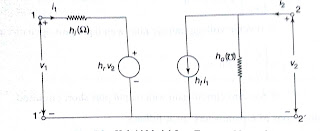
30.Draw the H parameter
equivalent circuit?
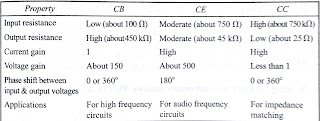
31.Compare CB,CE,CC
amplifiers, and what are the applications?




















Super sir thanks
ReplyDeleteNice questions
ReplyDeleteThank you for your articles that you have shared with us. Hopefully you can give the article a good benefit to us. UCAT Practice Test
ReplyDeleteGadget Groot is an online platform, here you will find all kinds of gadgets, mobile accessories, electronic devices, home appliances, etc. If you love gadgets and electronics devices then you must visit the Gadget Groot blogging website.
ReplyDeleteHello your blog is looking good. Thanks for sharing this information and keep posting.
ReplyDeleteif anyone is looking for more infromation content Western Sports Centre (WSC) vision is to be the premier provider of sports and coaching facility for all. We place great emphasis on excellence in customer relationship, teamwork, safety, respect, ethics and integrity
Cricket bat melbourne
If you want to buy exciting gadgets like- mobile accessories, headphones, earphones, earbuds, etc. Gadget Groot is an excellent platform they give review to all types of electronic gadgets and devices. For more information visit:- https://gadgetgroot.com/
ReplyDelete