Rectifiers:
1.What is the difference b/w AC and DC supply, what are the advantages of each?
Ac supply is sinusoidal function of t, but Dc supply is constant for every time, dc can be storable but not Ac, Ac can transfer for a long distance but not Dc.
2.What is meant by regulation? Why is it required?
It is a measure change in the magnitude between the sending and receiving end of a component.
3.How to convert AC to DC?
Step down Transformer – Rectifier – Filter -- Regulator
4.What are the requirements of Linear mode power supply?
Should give minimum operable DC voltage at rated current, ripples should low, should have short circuit protection, over voltage protection, should independent of temparature changes
5.What is transformer and types?
Transformer works based on Induction Principle, when Two coils are placed nearly then voltage transfer exist,
Types: Step down, step up Transformer
6.What is rectifier, filter, regulators?
Rectifier coverts AC to pulsating DC
Filter coverts the pulsating DC to Fluctuating DC
Regulator convers fluctuating DC to exat DC
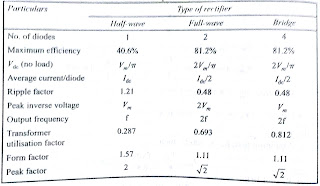
7.What are the various types in rectifiers and which one is best and why?
Half, Full wave , Bridge Rectifier. Bridge rectifier is best because PIV is less, efficiency more, ripple factor less, TUF is more, peak facor less, transformer cost is less.
8.Define ripple factor, efficiency, transformer utilization factor, form factor, peak factors?
Ripple factor= RMS value of ac component/Average value
Efficiency= dc output power / ac input power
TUF= dc power delivered to load/ac rating of transformer secondary
Form factor=rms/ average
Peak factor= peak value/ rms value
9.Define average value, RMS value, what is the significance of each?
Average is defined as sum per count, i.e mean. Or area of one cycle per time period
RMS is Root of Mean(average) of squares.
If data contains Both +,_ signs then average value can not give perfect idea about it, then Rms value gives idea about data.
10.Compare all rectifiers?
11.Explain the importance of ripple and regulation in the case of a rectifier.
Ripple factor gives the idea about fluctuations in signal, if it is less means ripples are less for DC ripple factor is Zero.
Regulation gives idea about the variation of DC output voltage as a function of DC load current
% regulation =(VNL-VFL)/VFL X 100% [ideal power supply its 0]
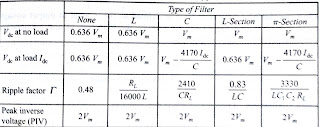
12.Explain why only the inductor or the capacitor alone is not used as filters to a FWR circuit.
In inductor filter Ripple factor is inversely proportional to load, In capacitor filter Ripple factor is proportional to load, so in LC filter ripple factor will be independent of load.
13.What are the different filters used in AC to DC converters? Which is best and why?
L,C,LC(L-section), π-section, RC filters. Best one is L-section because ripple factor is independent of load
14.Compare different filters?
15.Define line regulation and load regulation?
Line reg= change in output voltage/ change in input voltage
Load reg= (no load voltage- full load voltage)/ no load voltage
16.Define knee current?
It is the minimum amount of voltage which is required to operate Diode
17.Define knee current?
It is the minimum current through Zener diode in reverse bias
18.What are the different types of voltage regulators and which type is best, why?Zener diode voltage regulator, LM723, transistorized series and shunt regulators, best one is LM723 bcz its adjustable, short circuit protected, overvoltage protected