
Its not reliable, Noise effect is more on the signals, Power required for signal transmission also more, Circuit complexity is more and costly.
Reliable, Noise effect is very less, power consumption is very less, various Digital ICs are available so circuits not complex , cheap, Error detection and correction is also possible.
ASK, FSK, PSK, PCM, DPCM,Delta modulation, Adaptive Delta modulation etc..
Blocks: Anti aliasing filter, Sampler, Quantizer, encoder.
Sampler: converts a continuous time signal into discrete time signal.
Quantizer: converts continuous in amplitude signal into discrete in amplitude signal.
Pulse code modulation, Differential pulse code modulation, Delta modulation, Adaptive delta modulation.
Converting a continuous time signal into discrete in time signal is called as Sampling (similar to cutting a bread into slices)
To reconstruct the Continuous time signal from discrete time signal ,the sampling frequency should be more than equal to twice of Continuous time signal frequency(max).
If the sampling frequency is twice of Continuous time signal frequency(max), then that is called as Nyquist rate.
Impulse Sampling, Natural sampling, Flat top sampling.
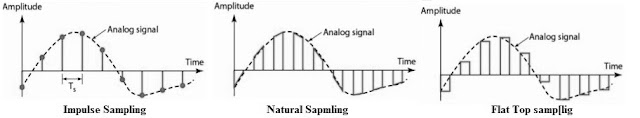
Due to imperfect sampling the signals will be interfered in frequency domain i.e called aliasing effect in sampling. if sampling theorem satisfied in sampling or first by passing signal from anti aliasing filter before sampling then aliasing effect will be reduced
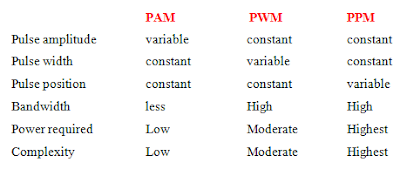
Pulse amplitude modulation, pulse width modulation and pulse position modulation..
The carrier pulse height (amplitude) proportional to amplitude of messege signal.
The carrier pulse width proportional to amplitude of message signal.
The carrier pulse position proportional to amplitude of message signal.
It represent the digital data as variations in amplitudes in carrier wave. i.e '1' represented by transmitting a fixed amplitude carrier wave for the bit duration with constant frequency.
It represent the digital data as variations in phase shift in carrier wave. i.e '1' represented by 0 phase shift carrier wave , where '0' represented as 180 phase shift incarrier wave for the bit duration with constant frequency
It represent the digital data as variation in frequency in carrier wave, i.e for '1' more than carrier frequency , for '0' less than carrier frequency.
for each one bit of binary data (0 & 1) carrier phase will be changed (two different shifts: 0, 180)
for each two bits of binary data (00,01,10 & 11) carrier phase will be changed (four different shifts : 45, 135, -45, -135)
22. What is the difference between Bit Rate and Baud Rate?
Bit rate represents Bits per sec,Baud rate represents no. of symbols per second i.e. in communications the no. of bits transmitted per sec is called as Bit Rate (units bps) and The no. of times a signal (here carrier) changes its state (change in freq, phase, amplitude) per sec is called as Baud rate.
23. What is bandwidth of BPSK signal?
2Fc, if Fc represents carrier frequency
24. Compare ASK, PSK and FSK.?
Bandwidth: ASK< PSK < FSK
Power: ASK <PSK = FSK
Probability of error: ASK > PSK > FSK
Signal to Noise Ratio: ASK < PSK < FSK
25. Why is ASK called as ON-OFF keying?







![x_{1}[n]*x_{2}[n]](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/c729fc738effd3f2e021a0aafd5b601e5636866e) ------------->
-------------> 
![x_{1}[n]x_{2}[n]](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/ef6743e17b24b69f8e3967724f056c04b779ee3e) ------------->
-------------> 


















